CF Møller Architects reveals Sweden’s tallest timber building
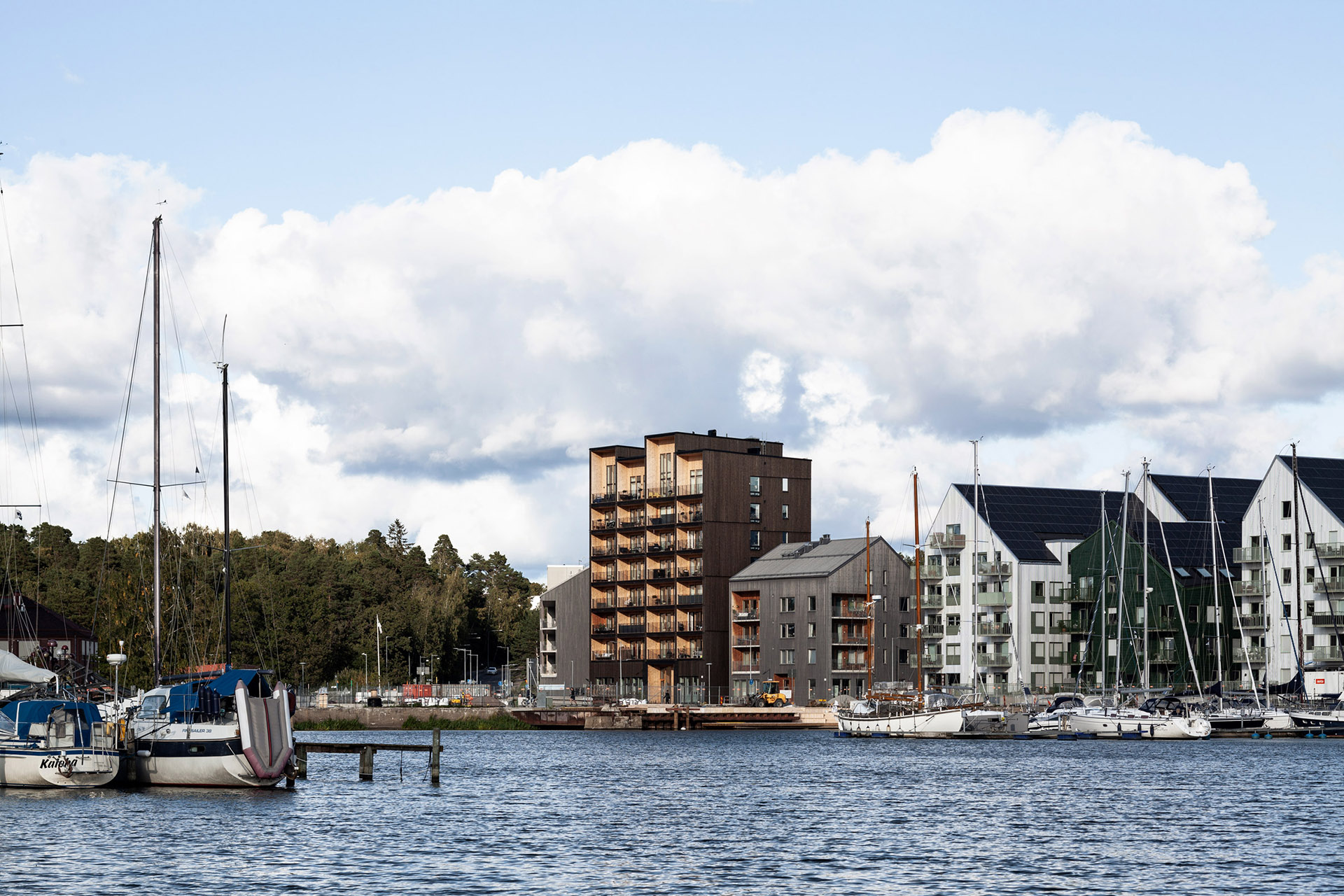
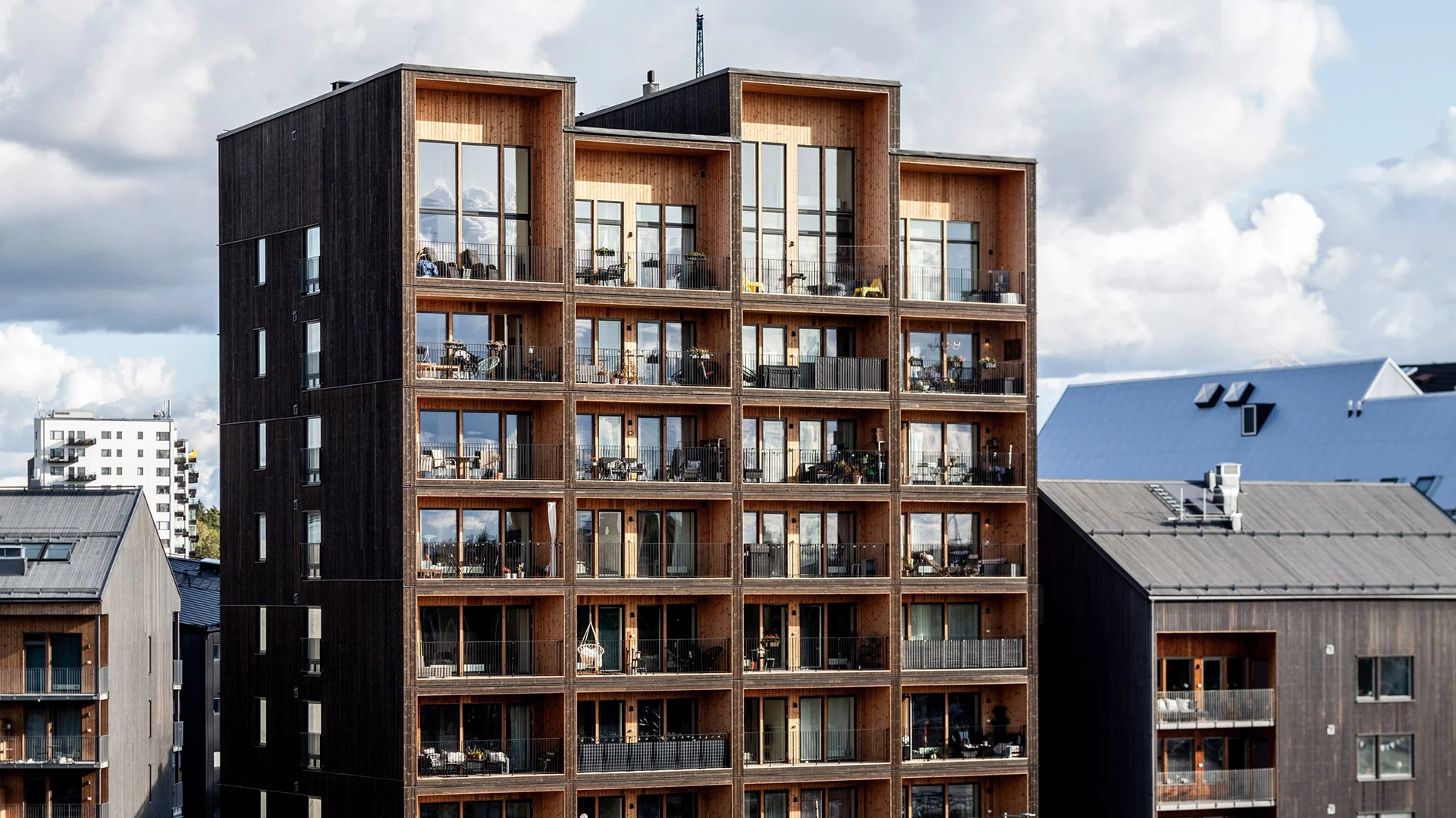
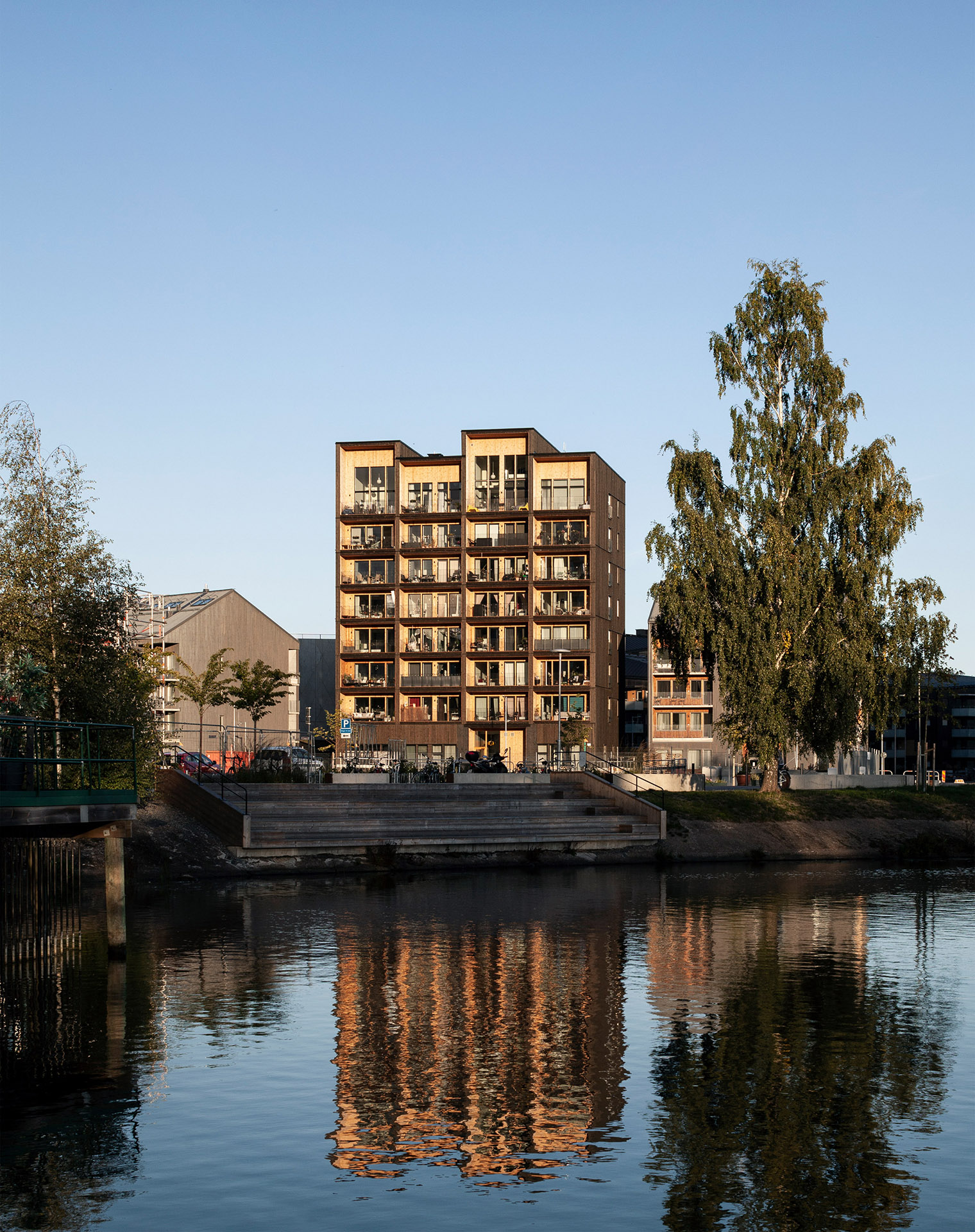
CF Møller Architects has revealed photos of the Kajstaden Tall Timber Building, which has recently completed in the city of Västerås and is Sweden’s tallest timber building.
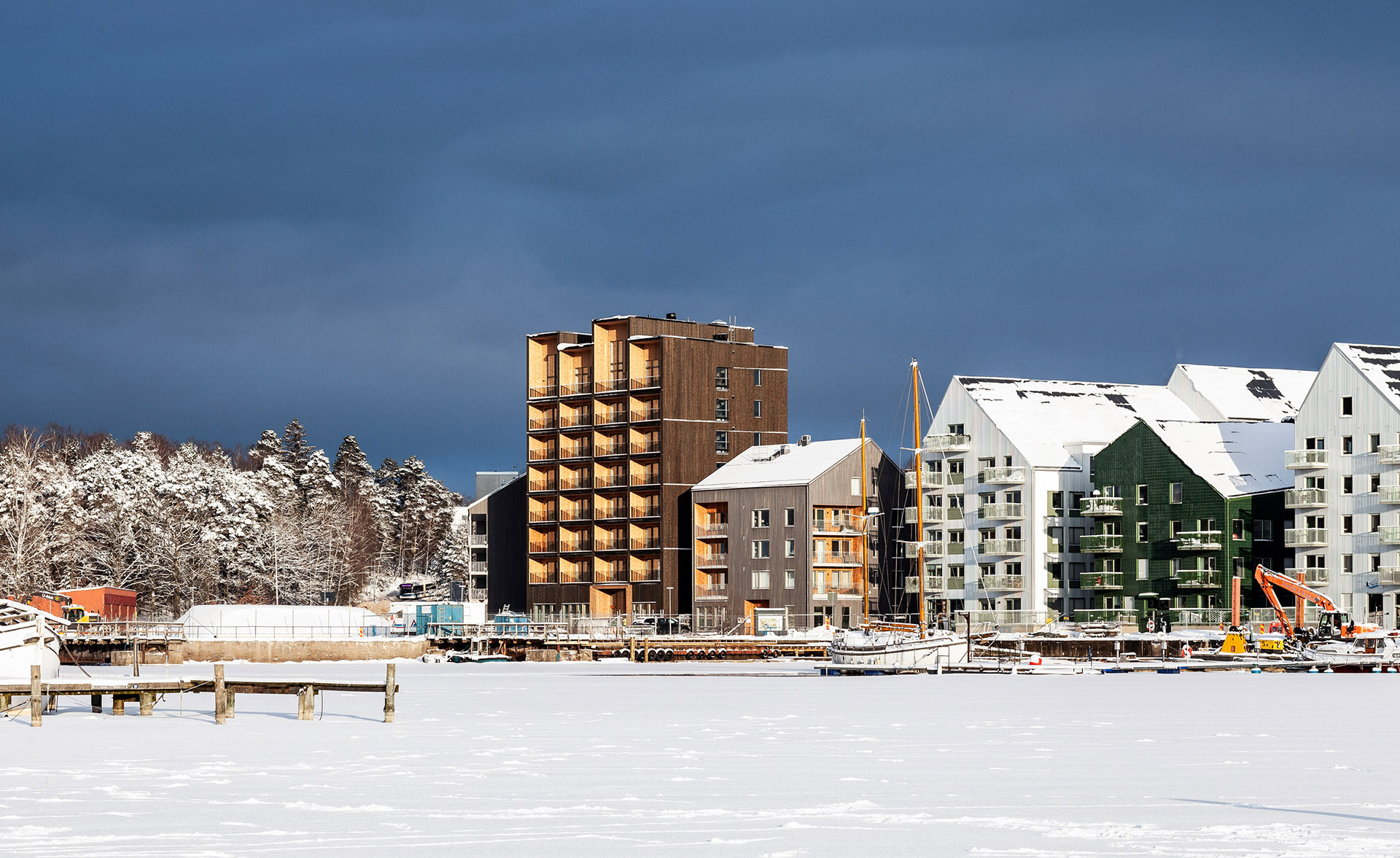
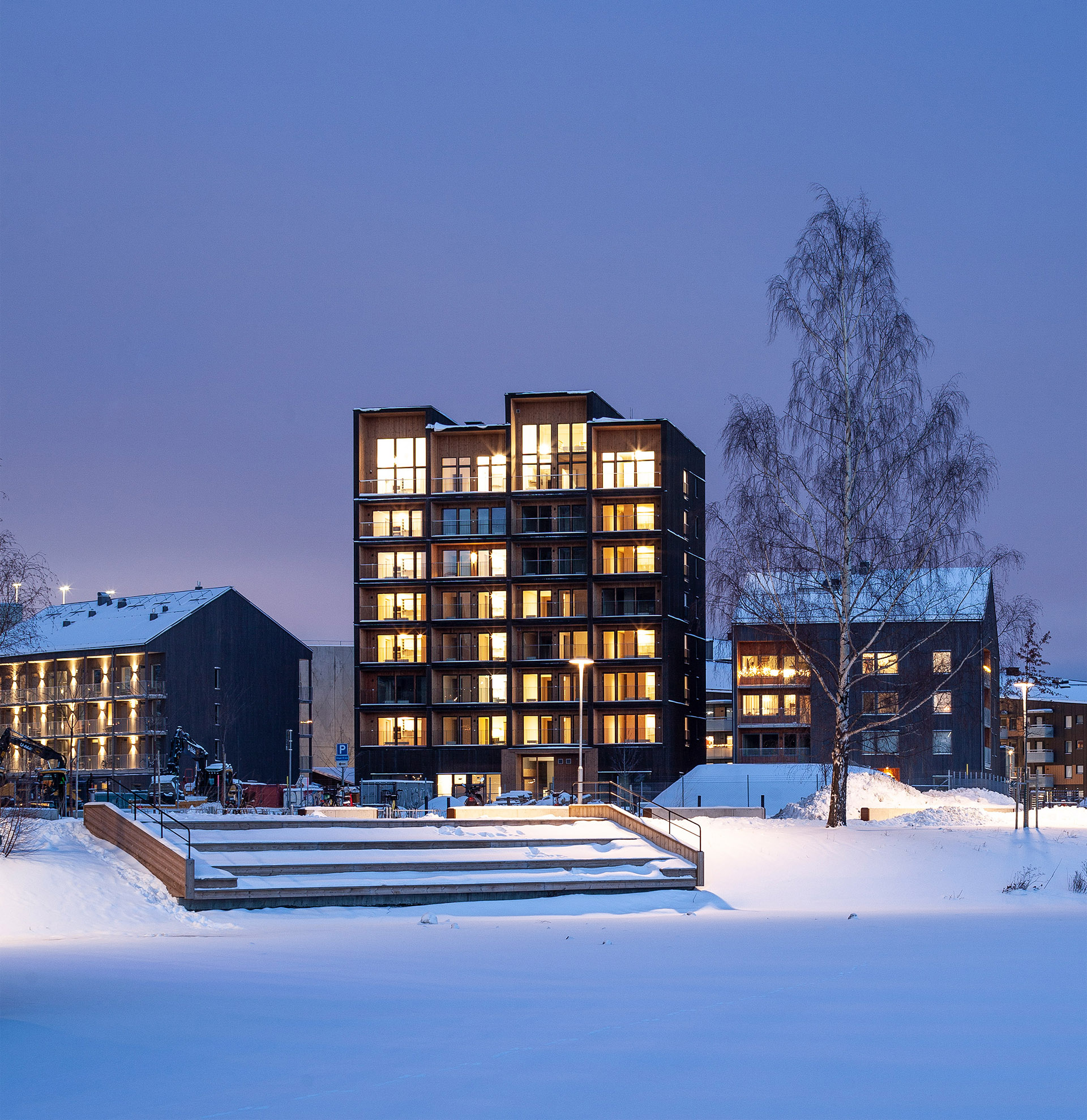
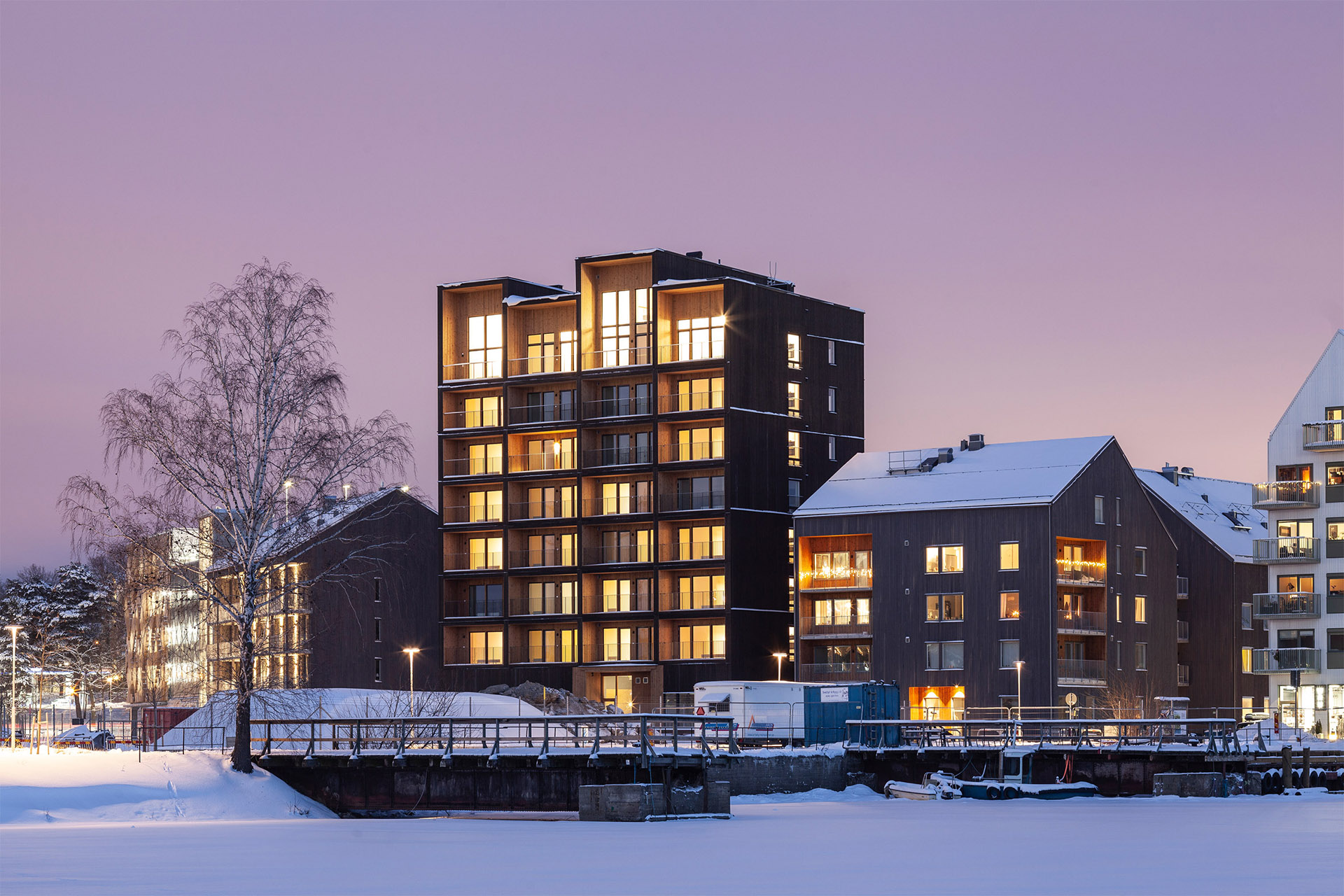
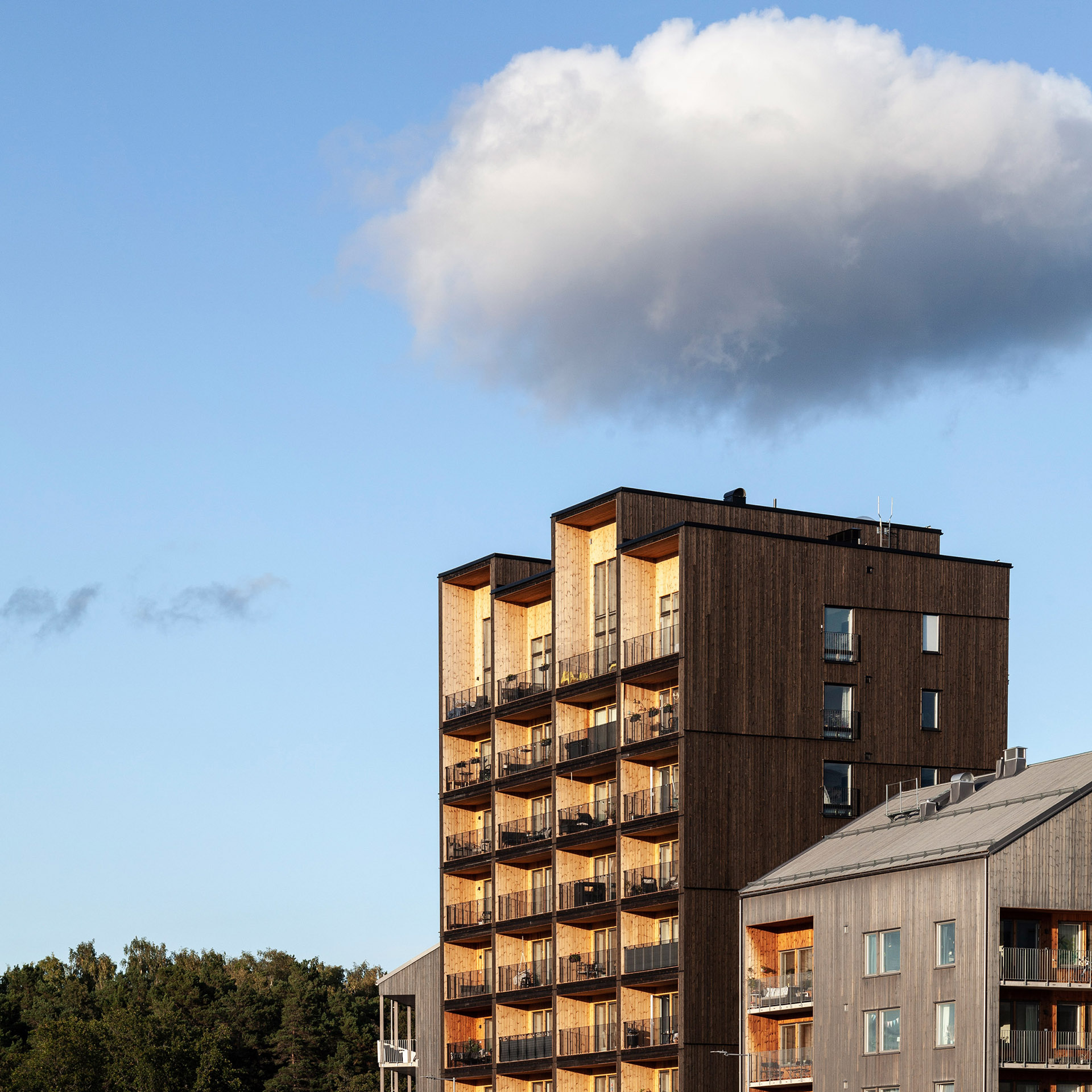
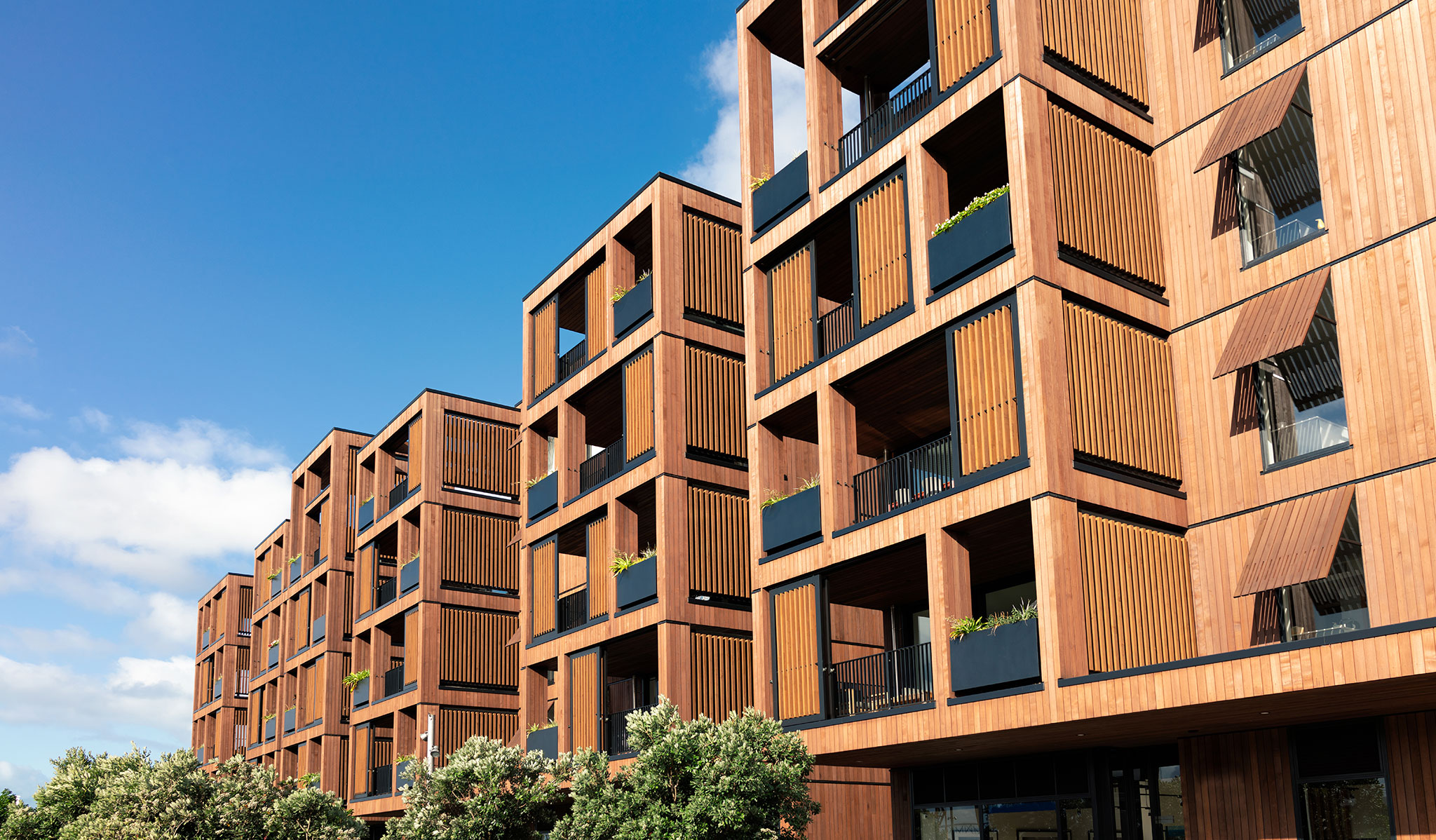
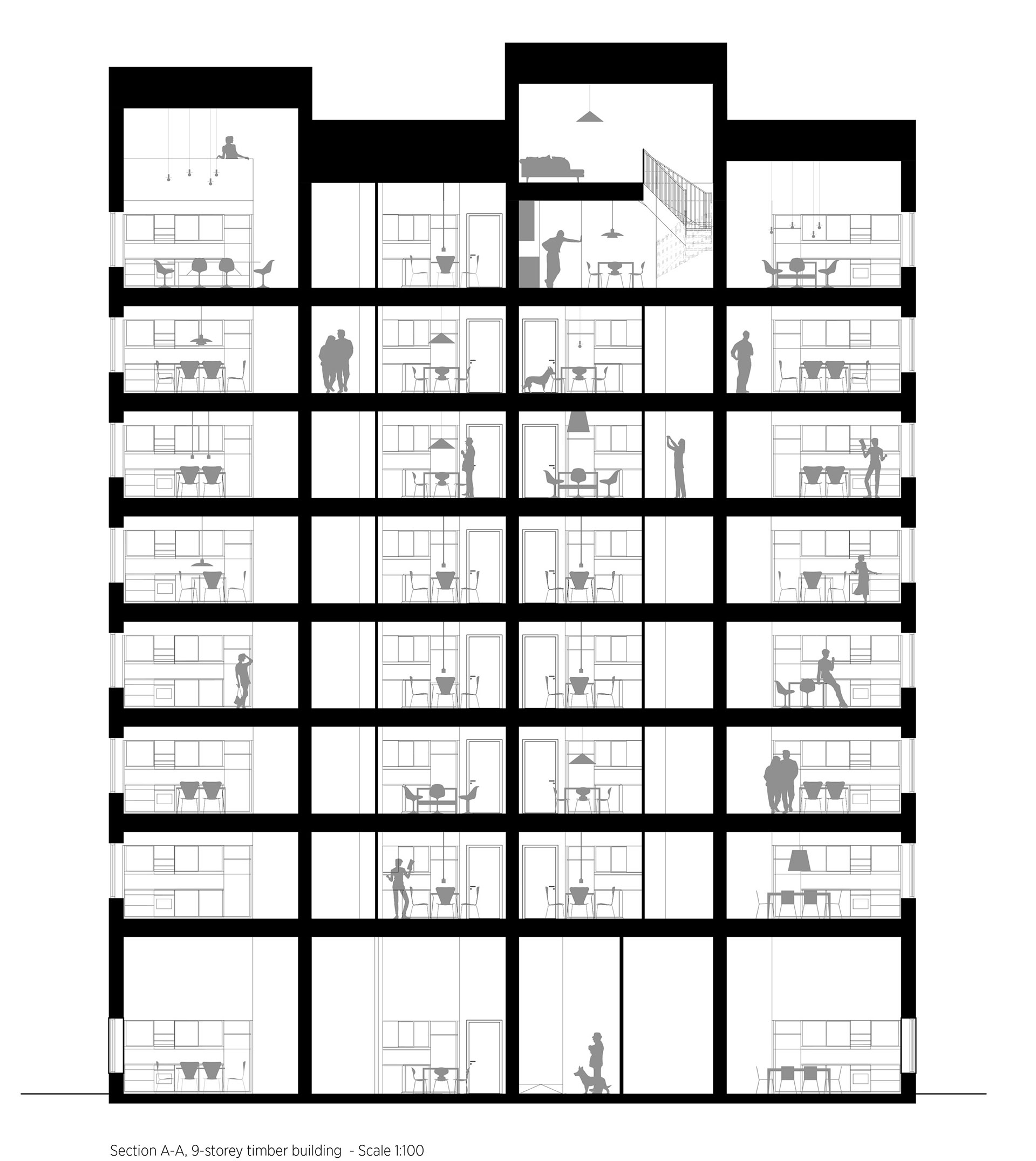
Completed in 2019, the 8.5-storey-high apartment block has a structure built entirely with cross-laminated timber, and secured with mechanical screws that ensure it can be taken apart and reused.

CF Møller Architects chose to use cross-laminated timber for the scheme as it is renewable, recyclable and has a lower carbon footprint than other traditional building materials like concrete. Wooden buildings are also believed to improve wellbeing of occupants when in use.
The studio hopes that the structure will become “a landmark for the area and a benchmark for a sustainable future”.

“The total carbon-dioxide savings from use of solid wood instead of concrete are estimated at 550 tonnes of CO2 over the building’s life,” explained Rob Marsh, the studio’s sustainability manager.
“The building in Kajstaden constitutes a new chapter in the history of construction, as it is currently Sweden’s tallest solid-timber building,” added associate partner Ola Jonsson.
“Through research projects and our other timber projects we have focused on innovation and contributed towards developing ways of realising high-rise buildings made of timber,” he continued

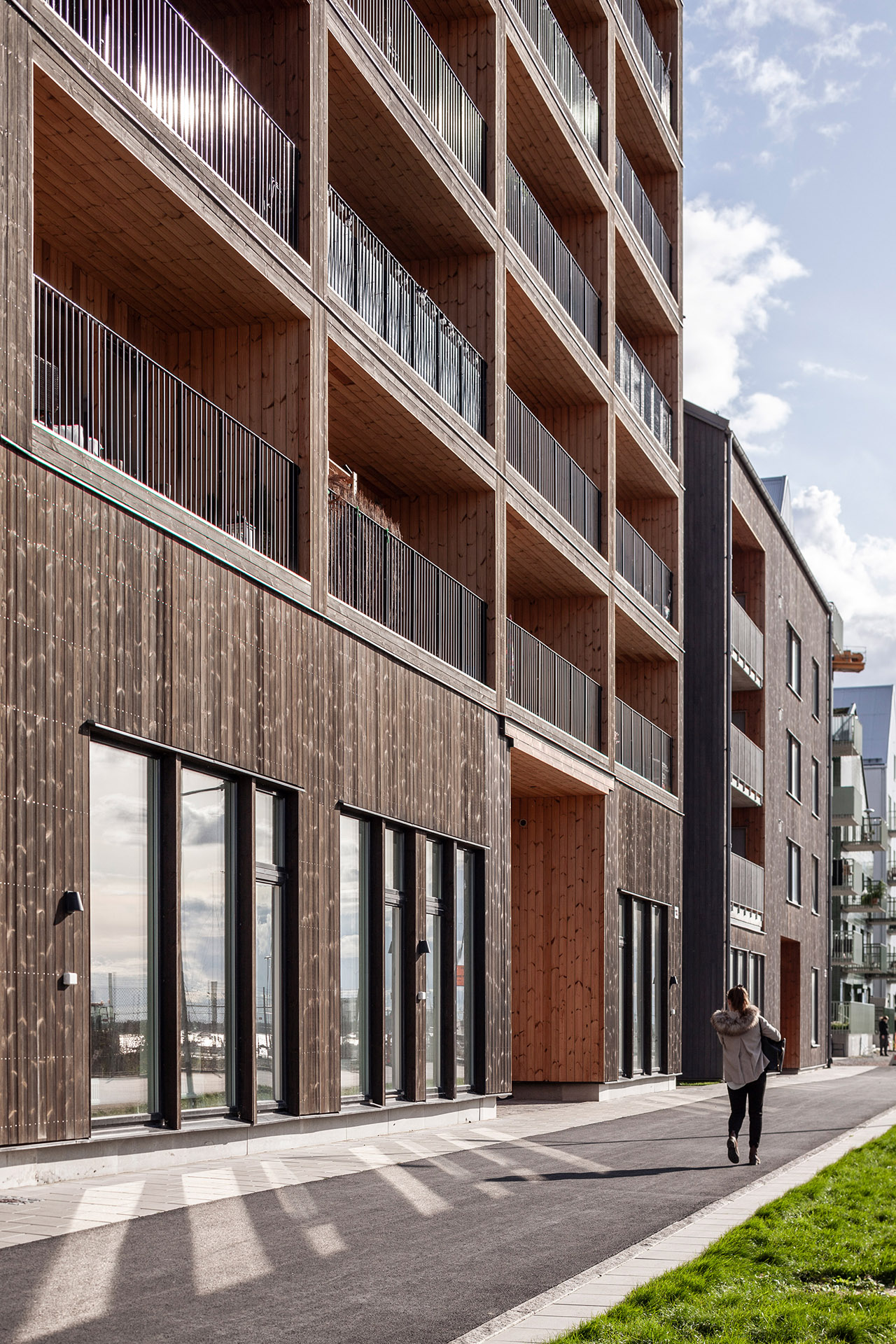
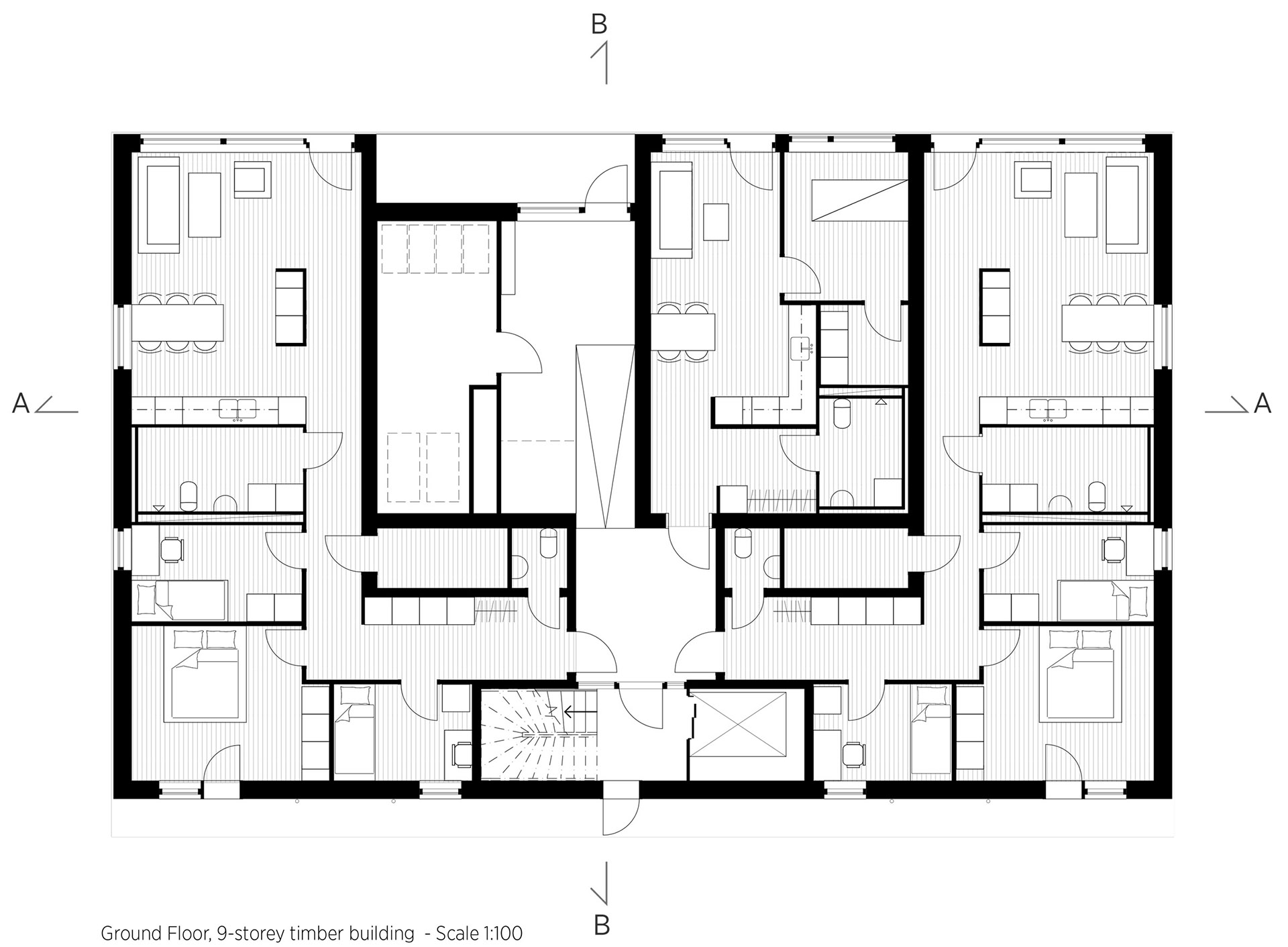
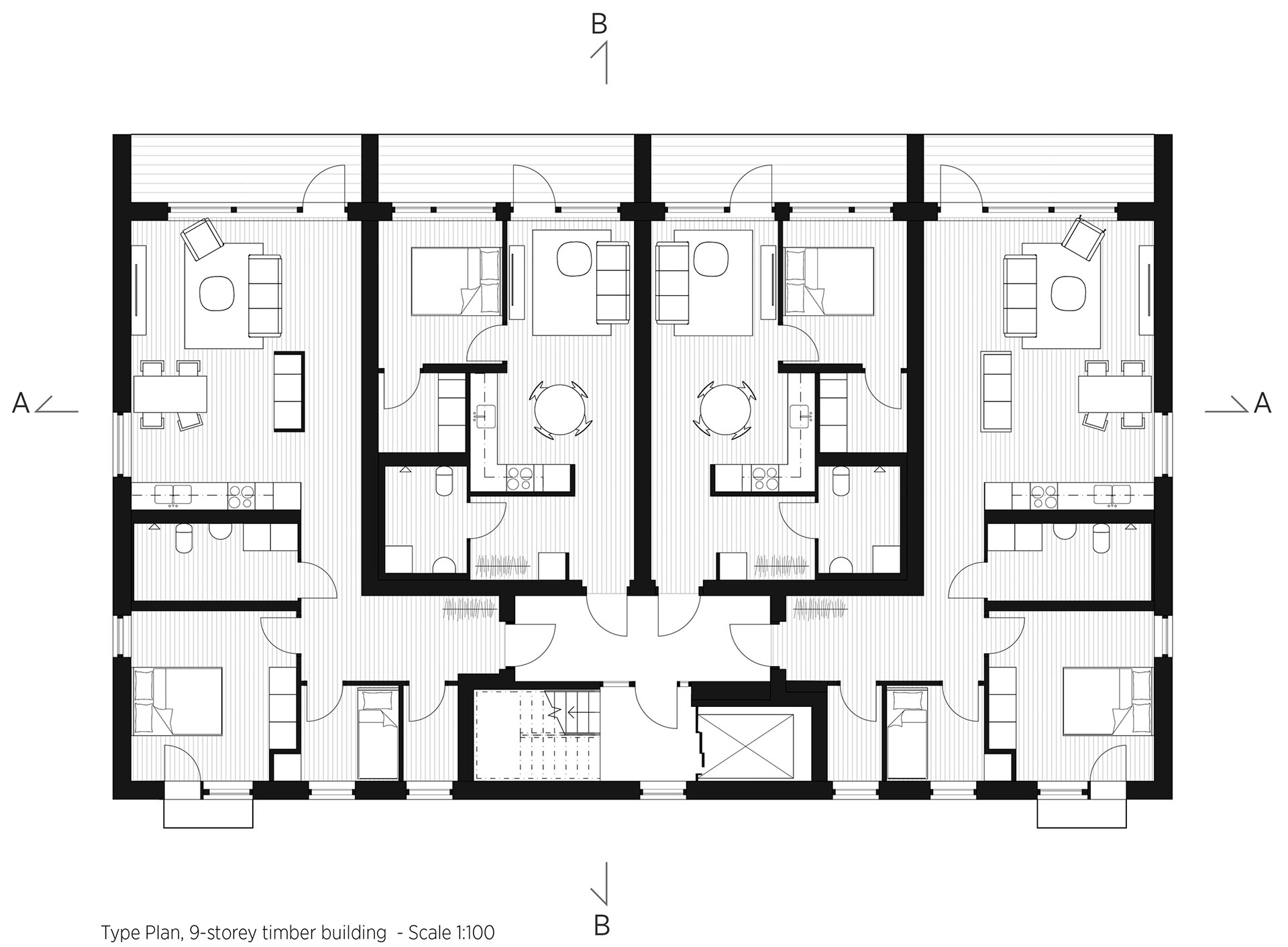
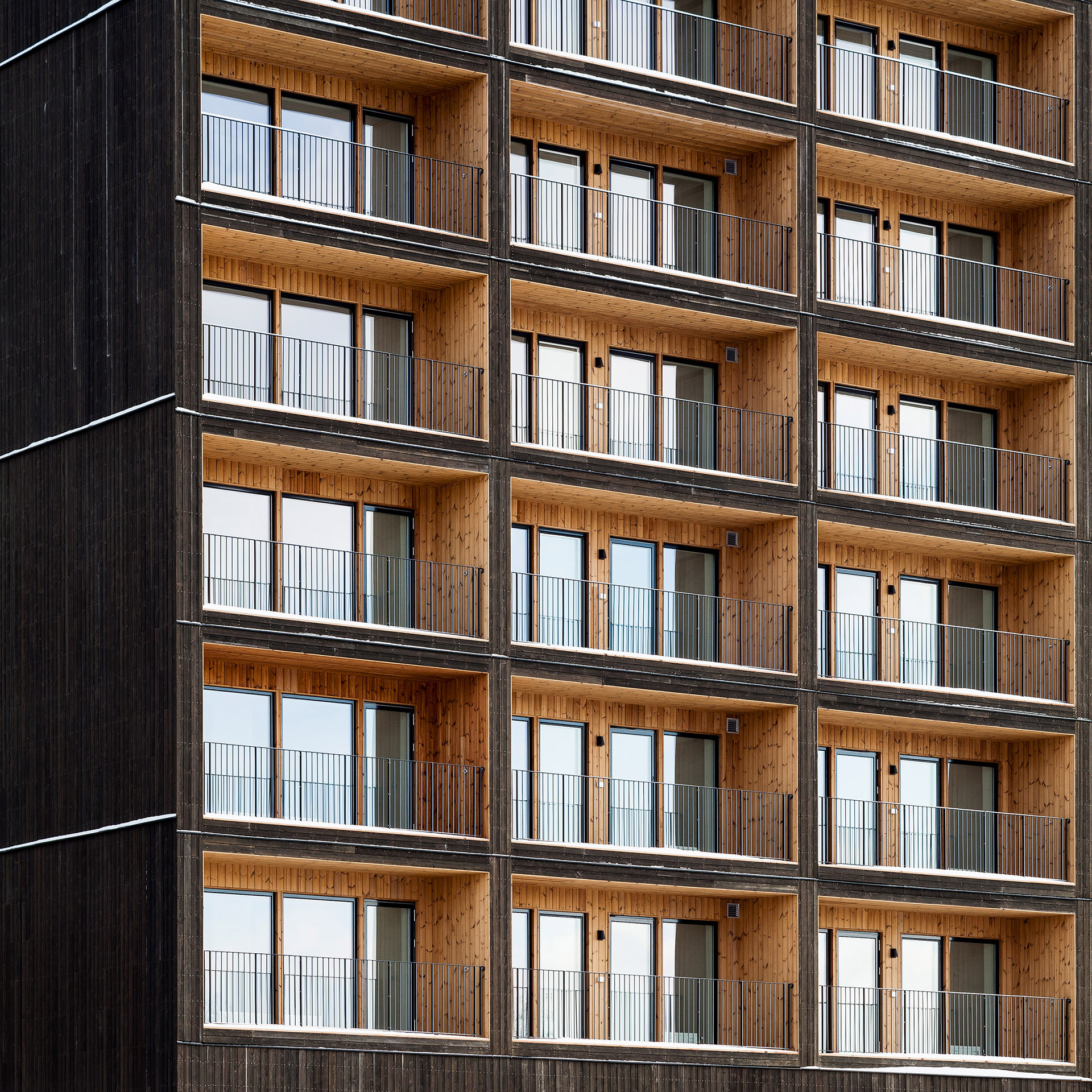
Inside, Kajstaden Tall Timber Building has four flats on each floor that range from one to five rooms in size. In a bid to maximise views and natural light, all the living rooms are positioned to look out over the harbour.
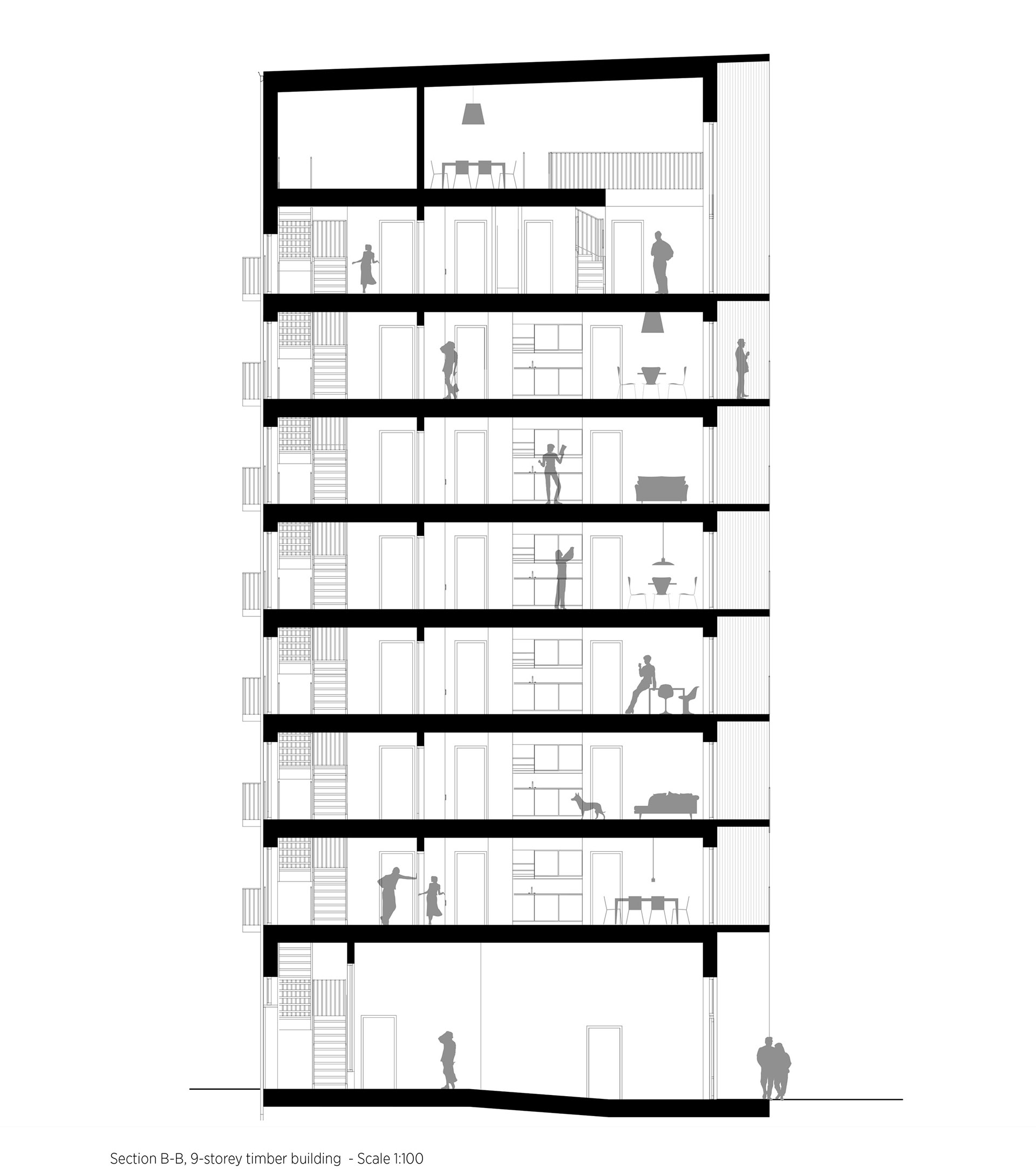
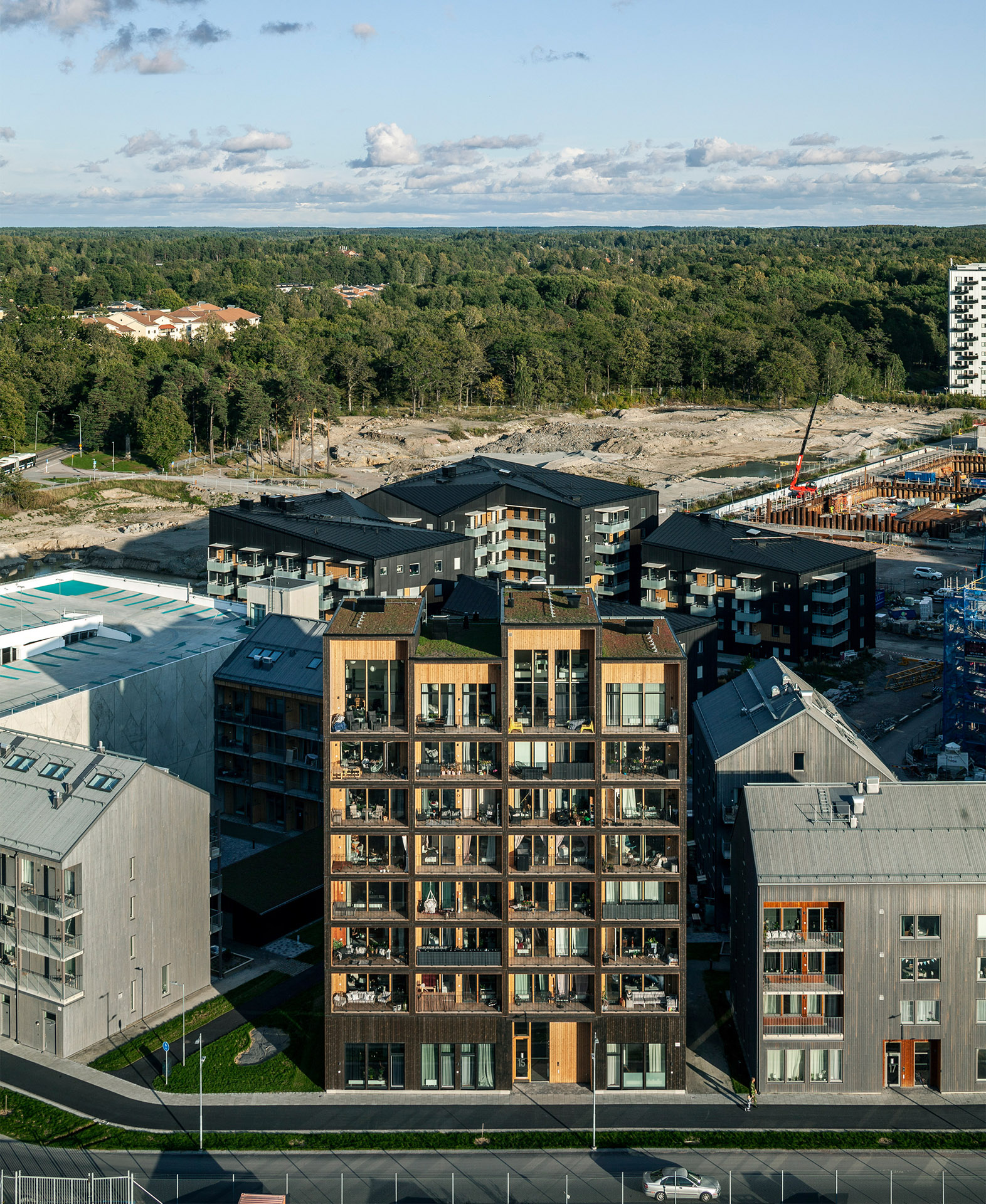
It is distinguished by its boxy form and staggered roof, created by double height apartments on the eighth storey. Each storey was constructed in just three days.

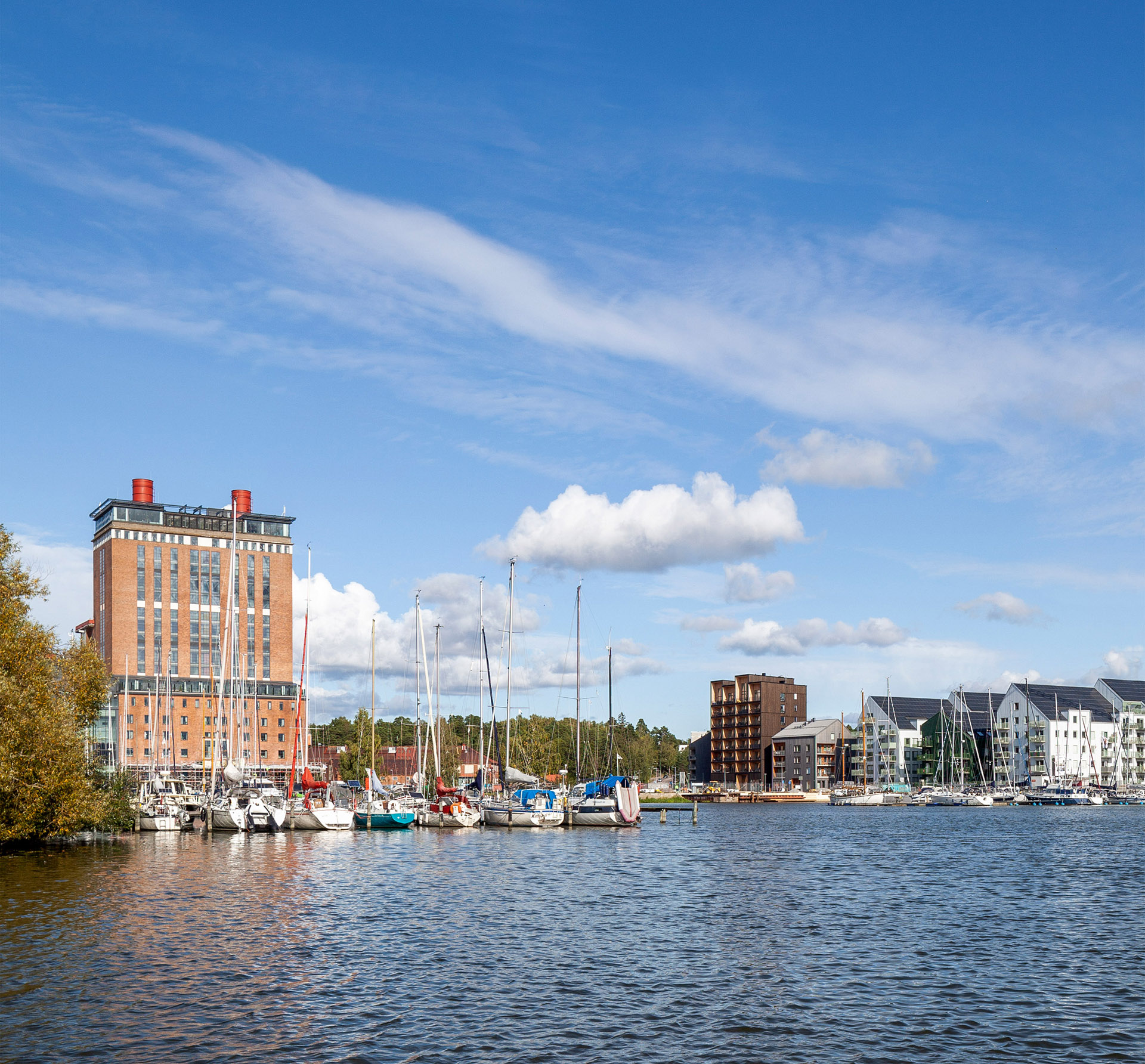
According to the studio, Kajstaden Tall Timber Building’s height and form is designed to complement surrounding landmarks and the aesthetic of its site in the industrial harbour.
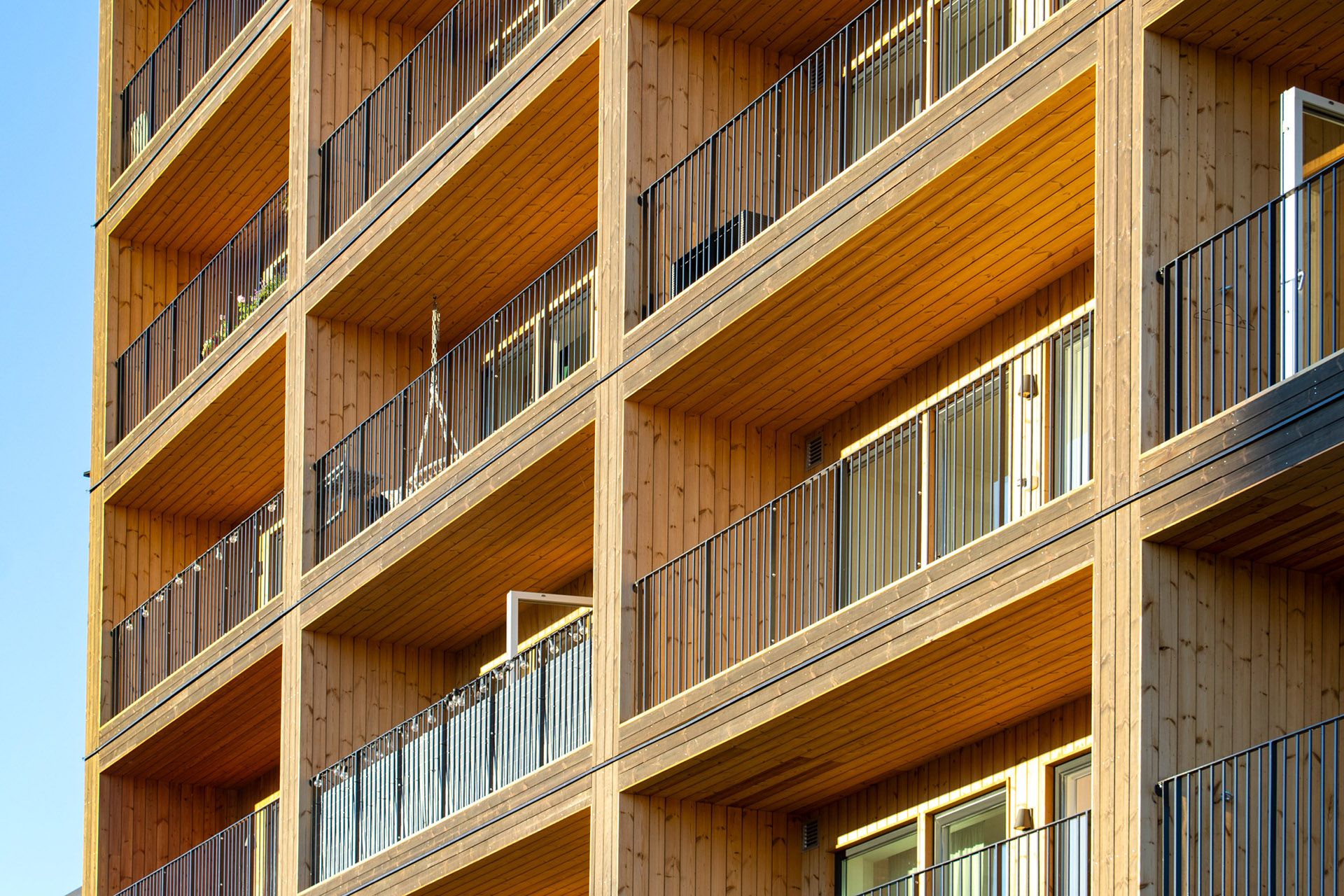
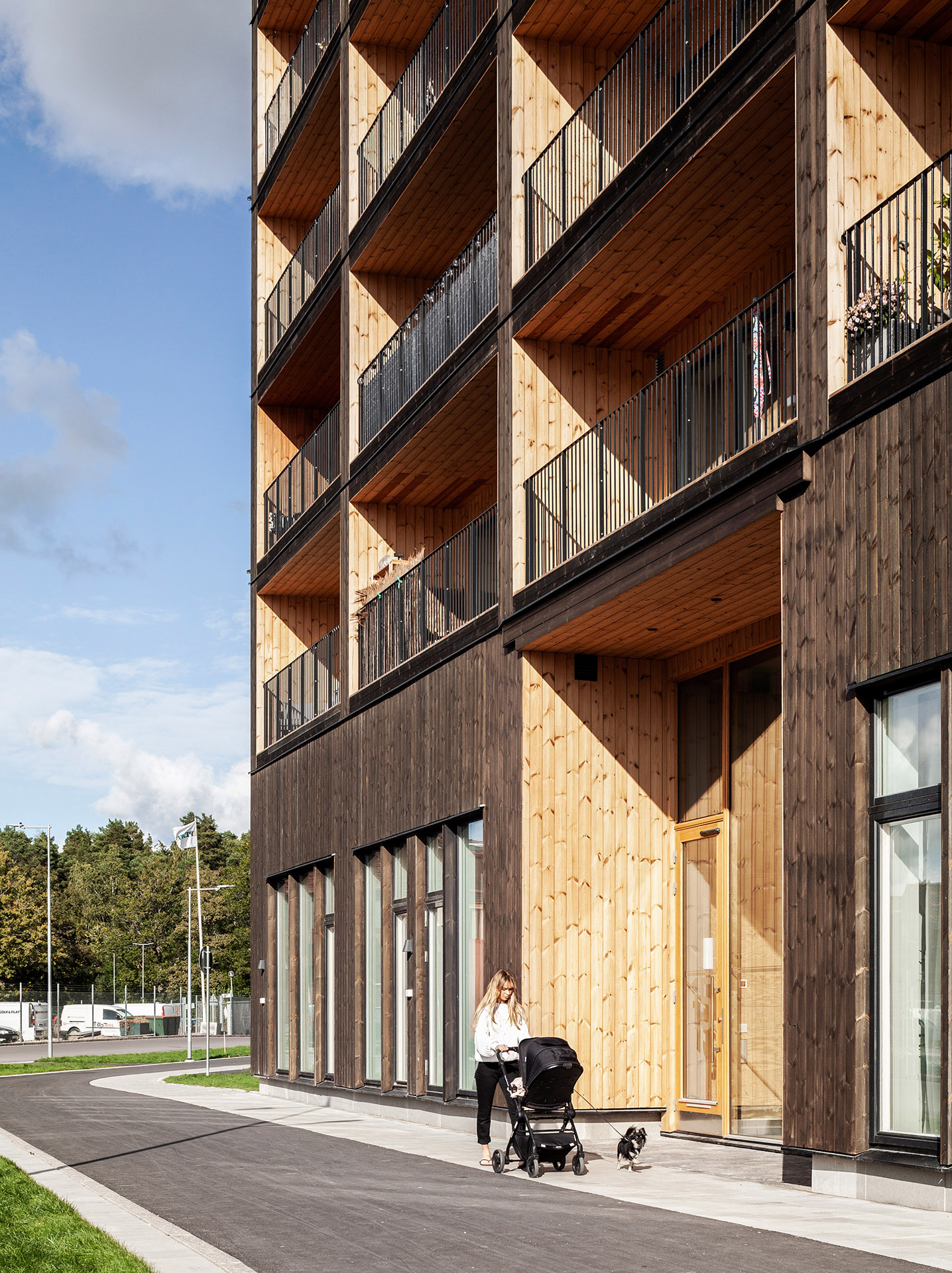
The building is wrapped by dark timber cladding made of stained thermowood – a type of Scandinavian softwood timber that has been heat treated for higher weather resistance.
These pigmented panels are contrasted with light, natural wood panels that line elements of the tower’s interiors, and each of the individual balconies.
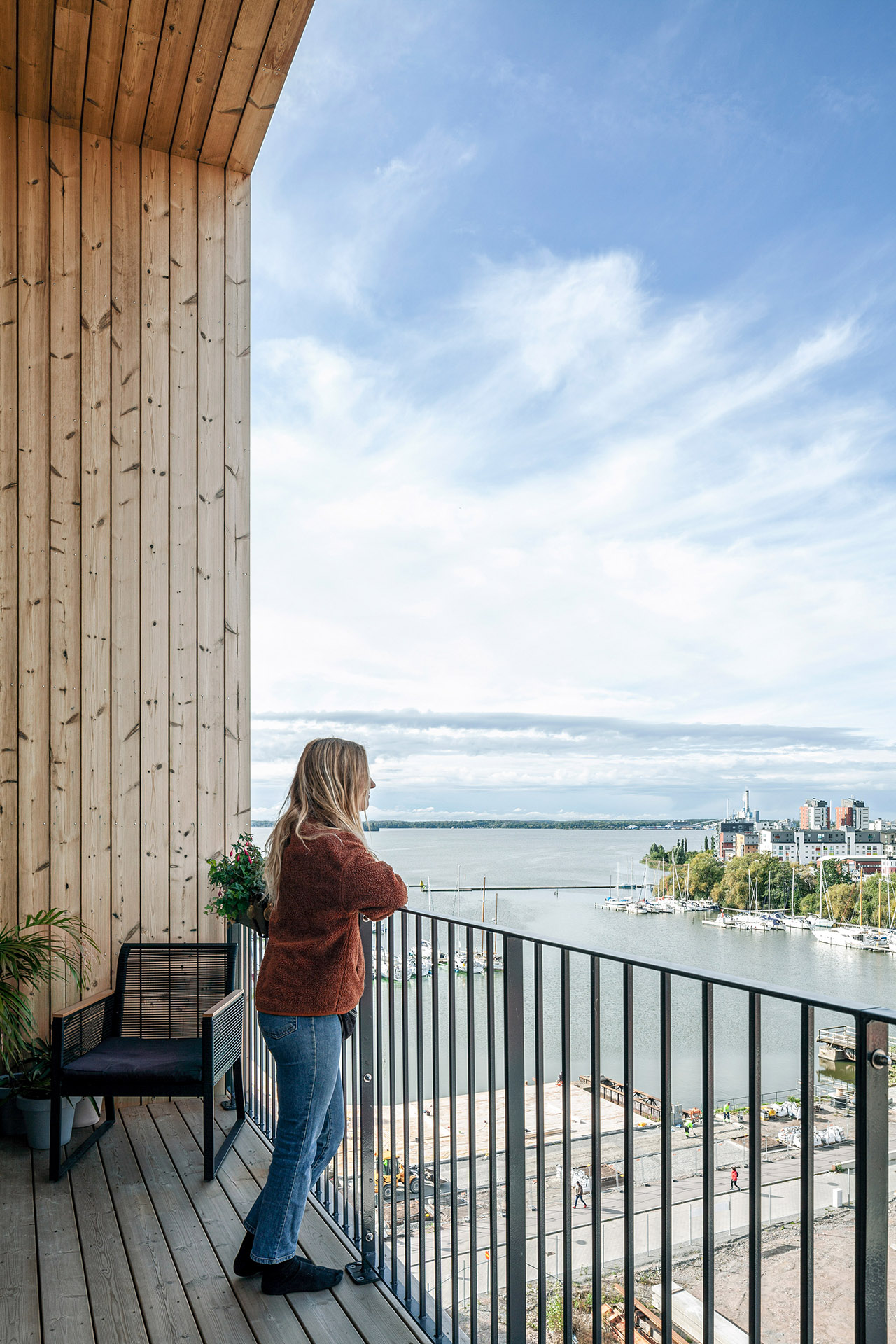

Kajstaden Tall Timber Building is complete with green roofs and greenhouses, which Jonsson said forms part of the building’s “holistic sustainable and bio-circular concept”.
CF Møller Architects is a Danish architecture studio founded by Christian Frederik Møller in 1924. Other recent projects by the studio the Lego office in Billund that incorporates giant bricks in its facade and a proposal for a plant-covered tower in Oslo.
Elsewhere, the architecture and urbanism arm of Google parent company Alphabet called Sidewalk Labs has recently unveiled a digital model of what would be the world’s tallest mass-timber building. It follows the company’s recent proposal for a mass-timber smart city in Toronto it has designed with Thomas Heatherwick and Snøhetta.
Photography is by Nikolaj Jakobsen.
Article: Lizzie Crook
Project credits:
Architect: C.F. Møller Architects
Landscape: C.F. Møller Architects
Contractor: Martinsons and Consto
Engineer: Bjerking
Know More
Timber in construction roadmap
Construção em Madeira,Porquê escolher madeira?
Government has introduced a statutory tree and woodland cover target which commits to increasing the tree canopy and woodland cover in England to 16.5% by 2050. But not only do we need to plant trees, we also need to make good use of the materials they provide to us.
O futuro da construção em madeira
A multiplicidade de materiais de construção à base de madeira abre uma vasta gama de possibilidades para os construtores de casas. Embora o método convencional de construção em betão, principalmente, aço ou alvenaria ainda dominem, cada vez mais projetos feitos de madeira são construídos todos os anos.
O Comportamento da Madeira ao Sismo
Construção em Madeira,Porquê escolher madeira?,Artigos
A madeira é um material com um excelente comportamento sísmico. É leve, os seus elementos construtivos apresentam grande capacidade de deformação e são sistemas de grande redundância.